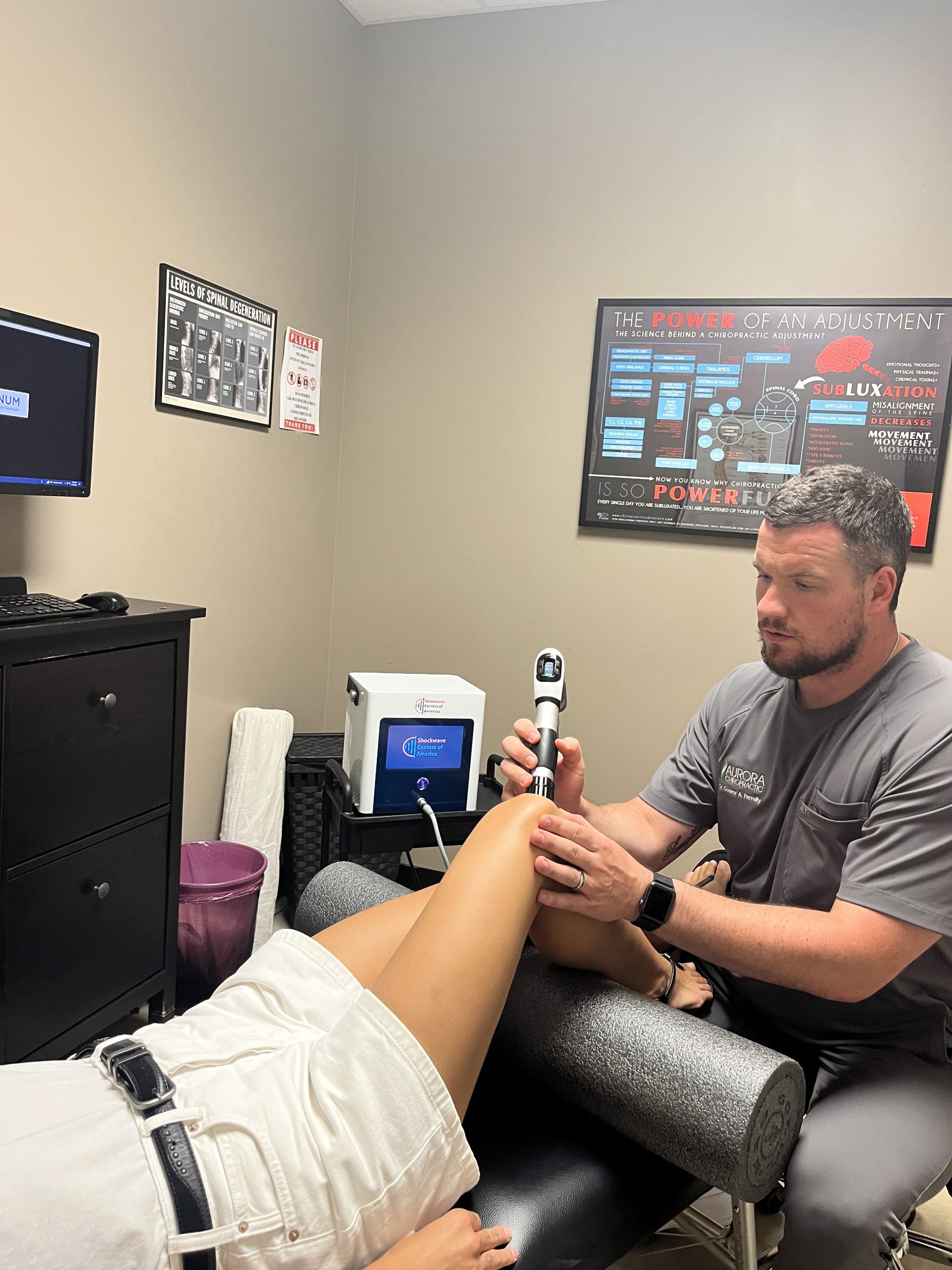
Shockwave therapy, or extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), uses high-energy acoustic waves to target painful areas and musculoskeletal tissues affected by subacute, subchronic, or chronic conditions. These waves stimulate biological responses that promote healing, tissue regeneration, and pain reduction.
The therapy increases blood flow, stimulates cell metabolism, and promotes neovascularization, aiding the repair of tendons, ligaments, bones, and surrounding soft tissues.
Shockwaves are characterized by a sudden jump in pressure, high amplitude, and non-periodic waveforms. This mechanical stimulation can help break down calcifications, release tissue adhesions, and reduce nerve sensitivity.
The energy is generated by a projectile propelled by compressed air. When the projectile strikes the transmitter at the end of the applicator, its kinetic energy is converted into acoustic energy, which is then delivered into the tissue at a precise depth.
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive, effective treatment option for chronic pain and soft tissue disorders, especially when other methods have not provided relief.
FAQ:
What is Shockwave Therapy used to treat?
- Shockwave therapy has been shown to be effective on a wide range of chronic conditions. Here are some examples of conditions where SWT has been shown to effectively treat symptoms and improved function:
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Tennis/Golfers Elbow
- Wrist/Ankle Pain
- Neuropathy/Nerve Pain
- Joint Pain (shoulder, knee, hip)
- Leg Pain
- Tendonitis
- Tendinopathies
- Bursitis, and more!
Does the Treatment Hurt?
- There may be a slight feeling of discomfort during the treatment, depending on the level of pain the patient is already experiencing in the area. However, most patients are able to tolerate this discomfort. Additionally, the intensity of the treatment can be adjusted throughout the session.
Watch this 2 minute educational video for more information!
Research Links
- A systematic review of shockwave therapies in soft tissue conditions: focusing on the evidence https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/48/21/1538.long
- Clinical application of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in orthopedics: focused versus unfocused shock waves
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22920552/
- High-energy versus low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy for calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder: which is superior?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24872197/
- Clinical efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31066293/